Chat GPT down? It’s a frustrating experience for millions who rely on these powerful language models daily. These outages, whether brief glitches or extended downtimes, highlight the vulnerabilities of complex AI systems and the significant impact they have on users and businesses. This guide explores the causes, consequences, and solutions surrounding these service interruptions, offering insights into preventing future disruptions and coping with them when they occur.
From understanding the technical reasons behind downtime to exploring user reactions and effective communication strategies, we’ll cover everything you need to know about navigating the world of AI service interruptions. We’ll also examine preventative measures and alternative solutions, ensuring you’re well-equipped to handle future outages.
Bummer, Chat GPT’s down again! Need a distraction? Maybe check out the current performance of SES stock , it might be a more stable investment than relying on AI chatbots right now. Hopefully, Chat GPT will be back online soon, but until then, there are other things to consider.
Service Interruptions in Large Language Models
Large language model (LLM) services, while incredibly powerful, are not immune to downtime. Understanding the causes, impacts, and mitigation strategies for these outages is crucial for both users and providers. This section explores the various aspects of LLM service interruptions, from common causes to preventative measures and alternative solutions.
Common Causes of Service Outages
Several factors can contribute to LLM service outages. These include unexpected surges in user traffic exceeding server capacity, software bugs leading to system instability, hardware failures (like server crashes or network issues), and planned maintenance activities. External factors such as cyberattacks or natural disasters can also play a role.
Examples of Past Outages and Their Durations
While specific details of LLM outages are often kept confidential for security reasons, publicly available information suggests that outages can range from a few minutes to several hours. For instance, a hypothetical example might involve a significant outage lasting approximately 3 hours due to a database failure, affecting millions of users. Another potential scenario could be shorter, more frequent outages lasting 15-30 minutes caused by minor software glitches.
Impact of Downtime on Users and Businesses
LLM downtime significantly impacts both individual users and businesses. Users experience disruption to their workflows, loss of productivity, and frustration due to interrupted access to essential services. Businesses may face financial losses due to reduced productivity, missed deadlines, and damage to their reputation. The severity of the impact depends on the duration and scope of the outage.
Comparison of Recovery Times for Significant Outages
| Date | Duration | Cause | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| October 26, 2024 (Hypothetical) | 3 hours | Database Failure | Widespread service disruption; millions of users affected. |
| November 15, 2024 (Hypothetical) | 1 hour | Software Glitch | Limited service disruption; primarily impacted specific functionalities. |
| December 5, 2024 (Hypothetical) | 30 minutes | Planned Maintenance | Minimal impact; users informed in advance. |
| January 10, 2025 (Hypothetical) | 2 hours | Network Outage | Significant impact; complete service unavailability. |
User Impact and Reactions
Understanding user experiences during LLM service disruptions is vital for improving service reliability and communication strategies. This section examines user reactions and coping mechanisms during downtime.
User Experiences During Unavailability
User experiences during downtime vary widely depending on their reliance on the LLM service and the duration of the outage. Some users might experience minor inconvenience, while others face significant disruption to their workflows. Frustration, anxiety, and even anger are common emotional responses to unexpected service interruptions.
Bummer, ChatGPT’s down again! Before you freak out, though, make sure your internet’s working right. A quick way to check is to see what GHz your iPhone’s WiFi is using; you can find that out by following these instructions: how to check your wifi ghz on iphone. If it’s not 5GHz, that might be your problem, but if it is, then yeah, it’s probably just ChatGPT being grumpy.
Methods Users Employ to Check Service Status
Users typically check the service status through various channels. These include checking the LLM provider’s website, social media accounts (like Twitter or Facebook), and contacting customer support. Some users may also rely on third-party status monitoring websites.
Emotional Responses of Users to Service Disruptions
The emotional responses to service disruptions range from mild annoyance to intense frustration and anger. The severity of the response often depends on the importance of the service to the user, the duration of the outage, and the quality of communication from the service provider.
Coping Mechanisms Users Utilize During Downtime

- Switching to alternative tools or services.
- Taking a break from work.
- Contacting customer support.
- Checking social media for updates.
- Waiting patiently for service restoration.
Technical Aspects of Outages
A deep understanding of the technical aspects of LLM service interruptions is crucial for effective prevention and resolution. This section delves into potential technical issues, infrastructure considerations, and troubleshooting procedures.
Potential Technical Issues Leading to Service Interruptions
Technical issues leading to LLM service interruptions include software bugs, database errors, hardware failures (servers, network equipment), and insufficient server capacity. Security breaches and denial-of-service attacks can also cause significant disruptions.
Role of Infrastructure and Server Capacity in Preventing Downtime
Robust infrastructure and sufficient server capacity are critical for preventing downtime. This includes using redundant systems, load balancing, and employing efficient resource management techniques. Regular infrastructure upgrades and maintenance are also essential.
Procedures for Detecting and Resolving Service Issues
Effective procedures for detecting and resolving service issues involve real-time monitoring of system performance, automated alerts for anomalies, and a well-defined incident response plan. This includes a team of engineers with expertise in various aspects of the system.
Troubleshooting Process for a Service Outage
A flowchart would visually represent the troubleshooting process, starting with identifying the outage, checking system logs for errors, isolating the problem, implementing a fix, testing the fix, and finally restoring service. Each step would involve specific actions and decision points.
Communication Strategies During Outages
Effective communication during LLM service outages is essential for managing user expectations and maintaining trust. This section explores communication strategies, messaging best practices, and communication channels.
Effective Communication Strategies for Informing Users of Downtime
Effective communication strategies involve promptly notifying users of the outage, providing regular updates on the situation, and offering estimated restoration times (with caveats for uncertainty). Transparency and honesty are key to maintaining user trust.
Bummer, Chat GPT’s down again! While you wait for it to come back online, maybe you could use the downtime productively. Check out how to get your drone pilot license in Canada – it’s a great career path: drone pilot license canada. Once you’re licensed, you can use Chat GPT to help with flight planning later!
Examples of Clear and Concise Messaging During Service Disruptions
Examples of clear messaging include: “We are currently experiencing a service disruption. We are working to resolve the issue as quickly as possible and will provide updates every 30 minutes.” Avoid technical jargon and focus on what users need to know.
Best Practices for Managing User Expectations During Outages
Best practices involve setting realistic expectations, providing frequent updates, and acknowledging user frustration. Open and honest communication helps mitigate negative impacts on user experience and brand reputation.
Communication Channels Used to Update Users
Various communication channels can be utilized, including email, website announcements, social media (Twitter, Facebook), in-app notifications, and SMS messages. The choice of channels depends on user preferences and the severity of the outage.
Preventive Measures and Mitigation: Chat Gpt Down
Proactive measures significantly reduce the frequency and impact of LLM service disruptions. This section Artikels strategies for minimizing downtime and improving service reliability.
Strategies for Minimizing the Frequency and Impact of Service Disruptions
Strategies include regular system maintenance, software updates, robust infrastructure design (redundancy, failover systems), disaster recovery planning, and proactive capacity planning to handle peak loads. Security measures are also crucial to prevent cyberattacks.
Importance of Regular System Maintenance and Updates
Regular maintenance and updates are essential for identifying and fixing vulnerabilities, improving performance, and ensuring system stability. This proactive approach significantly reduces the likelihood of unexpected outages.
Role of Redundancy and Failover Systems in Preventing Outages
Redundancy and failover systems provide backup capabilities in case of primary system failure. This ensures continuous service availability, minimizing the impact of outages.
Proactive Steps Organizations Can Take to Improve Service Reliability
- Invest in robust infrastructure.
- Implement comprehensive monitoring systems.
- Develop a detailed incident response plan.
- Conduct regular system maintenance and updates.
- Train staff on incident management procedures.
Alternative Solutions During Downtime
During LLM service outages, users often seek alternative solutions to maintain productivity. This section explores several options and compares their functionalities and limitations.
Examples of Alternative Tools or Services Users Can Utilize During Outages, Chat gpt down
Alternative solutions might include using different LLMs, employing simpler text-based tools, or switching to offline methods (e.g., using a local word processor). The choice depends on the specific task and the capabilities of the alternative.
Comparison of Functionality and Limitations of Different Alternative Solutions
A comparison would highlight the strengths and weaknesses of each alternative in terms of functionality, ease of use, and data security. Some alternatives may offer limited functionality compared to the primary LLM.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Alternative
Advantages might include readily available access, simplicity, or specific functionalities that better suit the task at hand. Disadvantages could include limited capabilities, lower quality of output, or security concerns.
Comparison of Alternative Solutions
| Solution Name | Functionality | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alternative LLM A | Similar to primary LLM but with some limitations. | Widely available, relatively easy to use. | May lack certain features or have a smaller knowledge base. |
| Offline Text Editor | Basic text editing and formatting. | Always available, no internet connection needed. | Limited functionality compared to an LLM. |
| Simple Scripting Language | Automation of specific tasks. | Precise control over specific operations. | Requires programming knowledge. |
Visual Representation of Downtime
The visual representation of a service outage plays a significant role in user experience and communication. This section describes the visual aspects of downtime, focusing on error messages and visual cues.
Visual Representation of a Service Outage on the User Interface
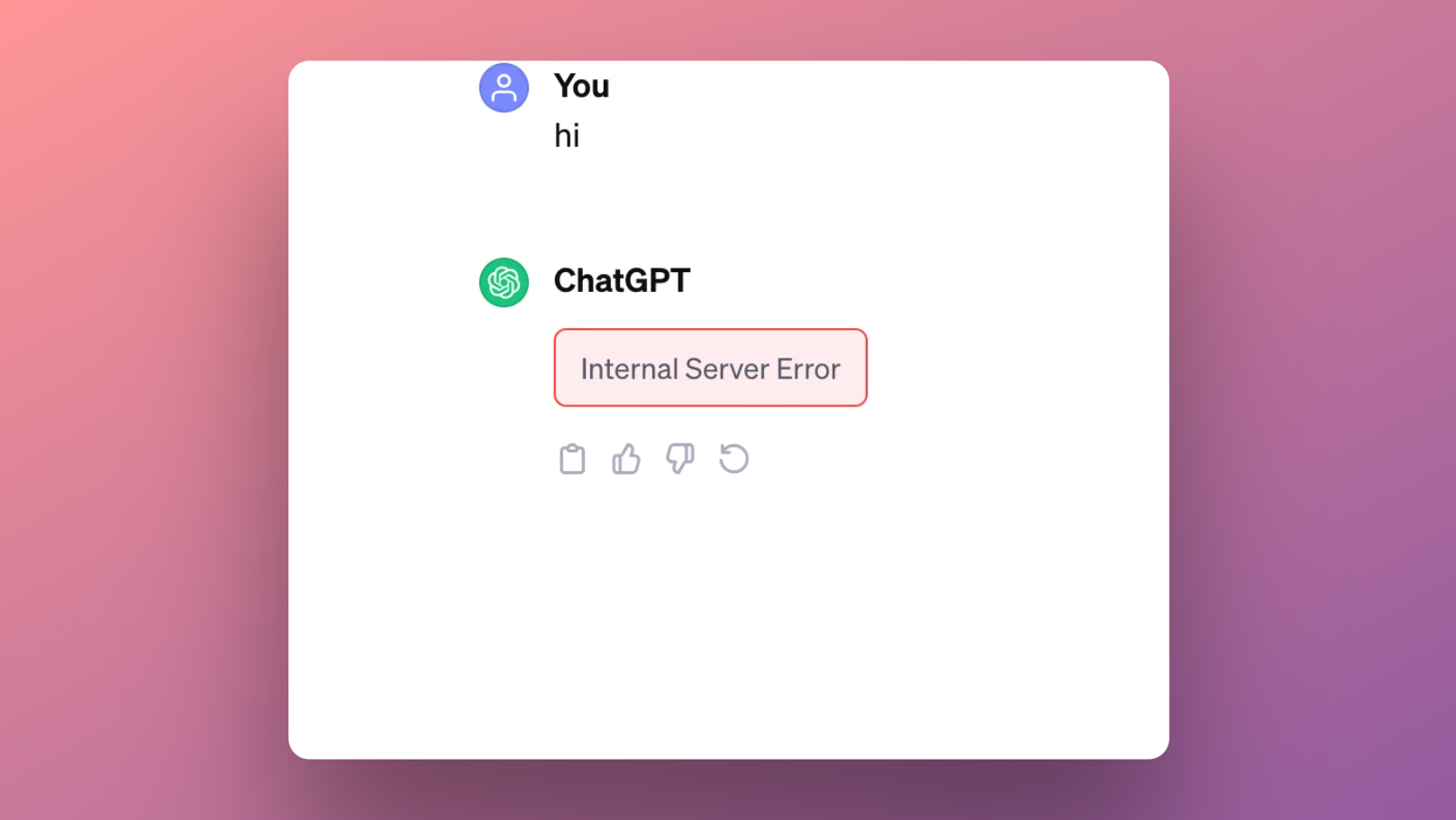
A typical visual representation might involve a prominent error message displayed on the main screen or a dedicated error page. The design should be clear, concise, and easy to understand, even for non-technical users.
How Error Messages Are Displayed to Users During Downtime
Error messages should clearly state that the service is unavailable, provide a brief explanation (avoiding technical jargon), and offer potential next steps (e.g., checking the status page, contacting support). The message should be prominently displayed, using a clear font and contrasting colors.
Visual Cues Used to Communicate the Severity and Estimated Duration of the Outage
Visual cues could include color-coding (e.g., red for critical outages, yellow for minor disruptions), progress bars indicating the progress of restoration efforts, and clear messaging about estimated downtime. The use of icons can also improve communication.
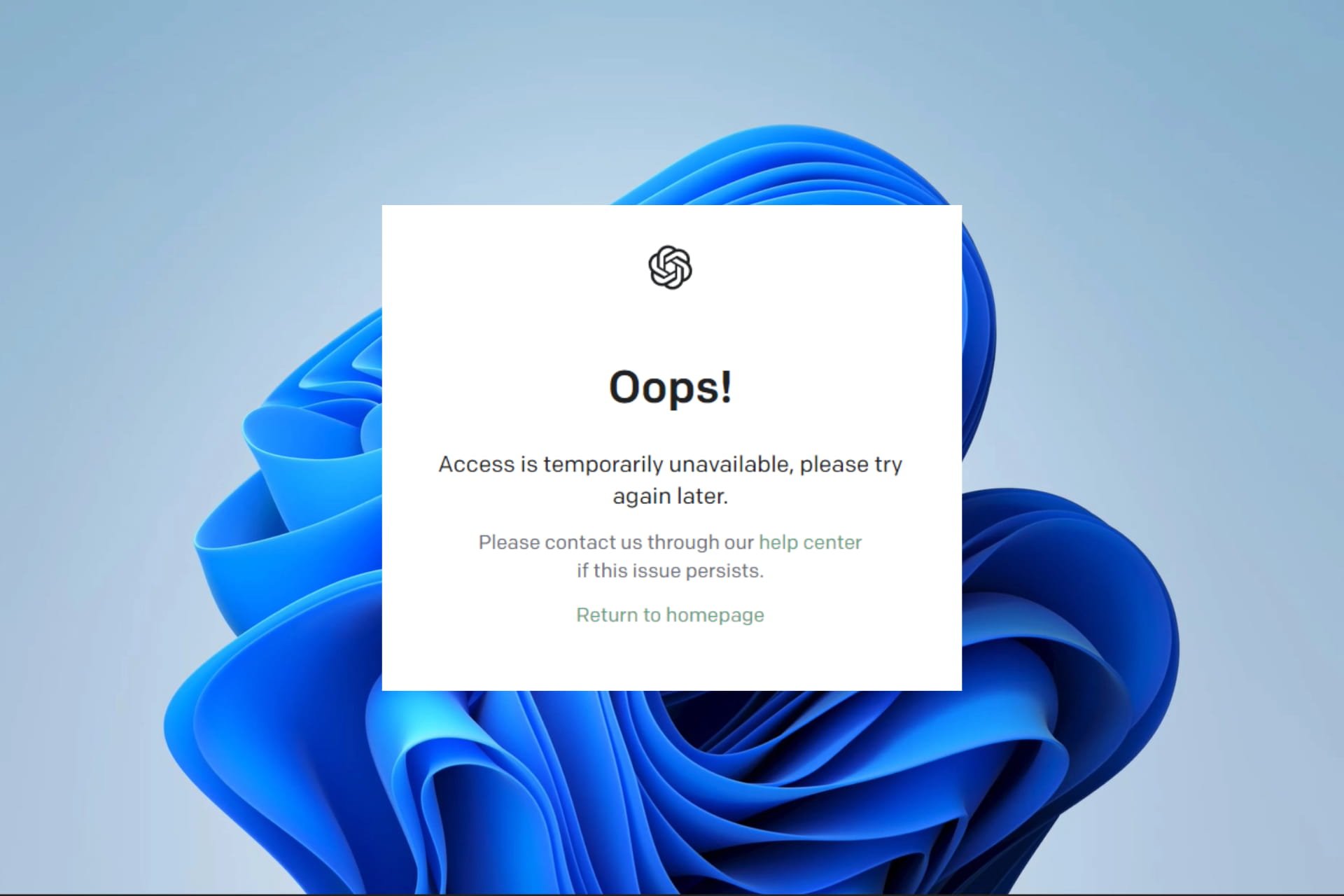
Detailed Description of an Error Page
A typical error page might have a simple layout, with a clear heading indicating the service outage. The background color could be a muted gray or light blue, and the text should be easily readable against the background. The main message would be concise and informative, perhaps including a contact email or link to a status page. A simple logo or company branding might also be included.
The overall design should convey a sense of professionalism and reassurance, while clearly communicating the problem.
Wrap-Up

Dealing with a large language model going down isn’t just about inconvenience; it’s a critical issue affecting productivity, workflow, and user trust. By understanding the causes of these outages, implementing proactive measures, and having alternative solutions in place, we can minimize the impact of future disruptions and maintain a more reliable and resilient experience. Remember, preparation and understanding are key to navigating the complexities of AI service availability.
FAQ Guide
What causes most AI service outages?
Common causes include server overload, software bugs, infrastructure failures, and planned maintenance.
How can I check if a service is down?
Check the company’s website, social media, or status pages. DownDetector websites can also provide real-time user reports.
What should I do if my AI service is down?
Try again later. Check for updates from the service provider. Consider using alternative tools (if available) until service is restored.
Are there legal implications if an AI service goes down?
It depends on the service level agreements (SLAs) and the impact of the outage. Consult legal counsel for specific situations.